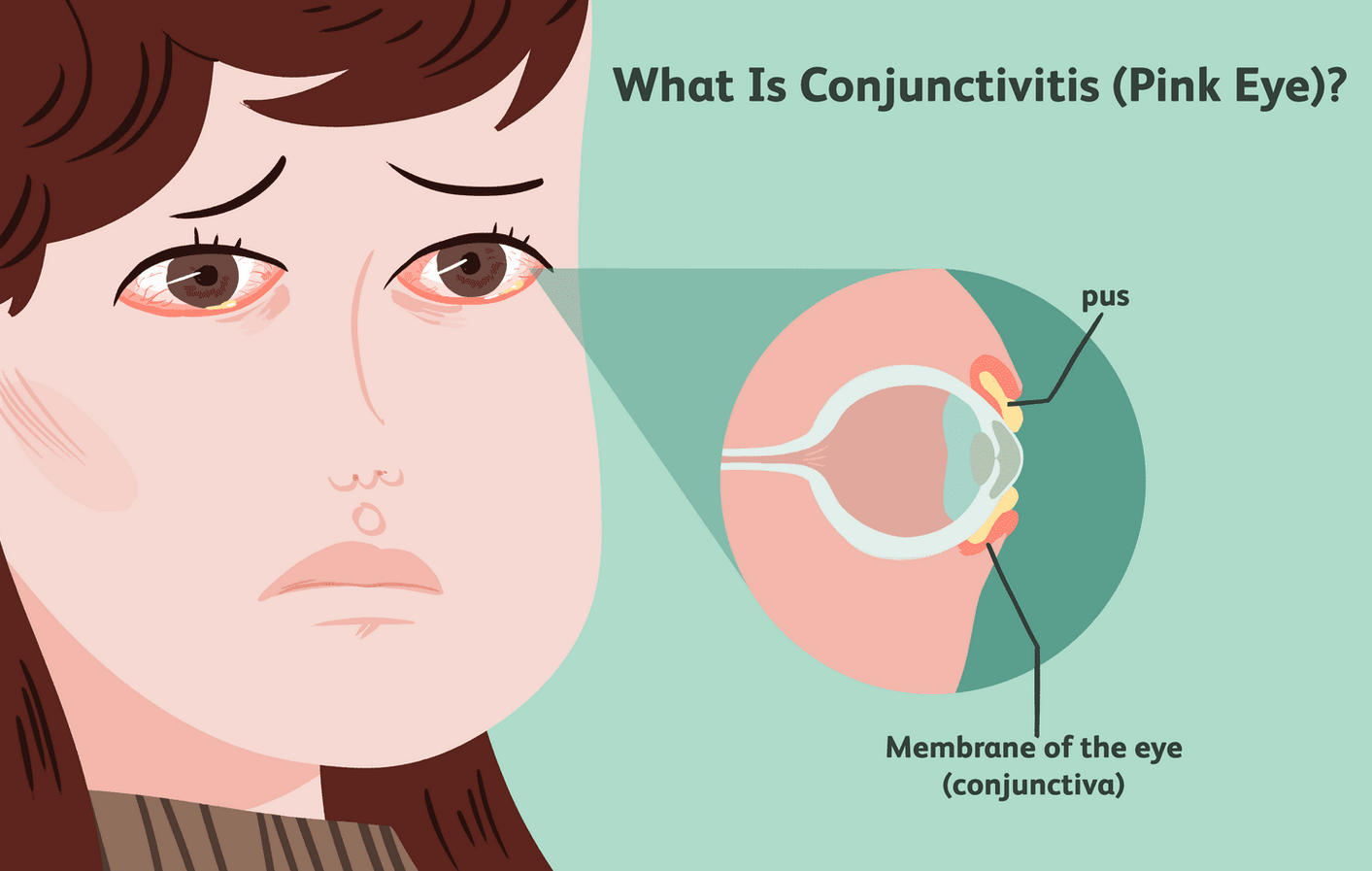
The research on meditation and mindfulness suggests that there is some evidence to support the idea that these practices can have positive effects on well-being and happiness. However, it's essential to acknowledge that scientific understanding is continually evolving, and new research may have emerged.
Here are some key points from the existing research up to September 2021:
- Stress Reduction: Many studies have shown that meditation and mindfulness practices can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression symptoms. By learning to focus on the present moment and cultivate a non-judgmental awareness, individuals may experience a sense of calm and relaxation.
- Increased Emotional Regulation: Mindfulness practices have been linked to improved emotional regulation. By being more aware of one's emotions and thoughts, individuals may be better equipped to respond to challenging situations with less reactivity.
- Brain Changes: Neuroscientific research has indicated that meditation can lead to changes in brain structure and function. For example, it may increase the volume of brain regions associated with emotional regulation and attention.
- Quality of Life: Some studies have shown that regular meditation or mindfulness practice can enhance overall life satisfaction and subjective well-being.
- Enhanced Empathy and Compassion: Practicing mindfulness has been associated with increased feelings of empathy and compassion towards oneself and others.
However, it's essential to recognize that the effects of meditation and mindfulness can vary between individuals, and not everyone may experience the same benefits. Additionally, the quality of scientific studies can influence the strength of the evidence, and more rigorous research is still needed in some areas.
Furthermore, happiness is a complex and multifaceted construct, making it challenging to measure and draw clear-cut conclusions about causality. It's essential to approach any claims about meditation and mindfulness with a critical and open-minded perspective.